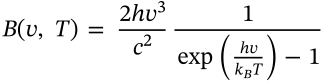Velocity
velocity motion
$$v = \frac{\mathrm{d}r}{\mathrm{d}t}$$
v = \frac{\mathrm{d}r}{\mathrm{d}t}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>v</mi><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><mi>d</mi><mi>r</mi></mrow><mrow><mi>d</mi><mi>t</mi></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
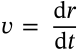
Acceleration
acceleration motion
$$a = \frac{\mathrm{d}v}{\mathrm{d}t} = \frac{\mathrm{d}^2r}{\mathrm{d}t^2}$$
a = \frac{\mathrm{d}v}{\mathrm{d}t} = \frac{\mathrm{d}^2r}{\mathrm{d}t^2}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>a</mi><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><mi>d</mi><mi>v</mi></mrow><mrow><mi>d</mi><mi>t</mi></mrow></mfrac><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><msup><mi>d</mi><mn>2</mn></msup><mi>r</mi></mrow><mrow><mi>d</mi><msup><mi>t</mi><mn>2</mn></msup></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
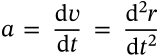
Newton's Second Law of Motion
newton's second law of motion motion
$$F = ma$$
F = ma
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>F</mi><mo>=</mo><mi>m</mi><mi>a</mi></mrow></math>
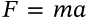
Universal Graviation
universal graviation gravity
$$F = G \frac{m_1 m_2}{r^2}$$
F = G \frac{m_1 m_2}{r^2}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>F</mi><mo>=</mo><mi>G</mi><mfrac><mrow><msub><mi>m</mi><mn>1</mn></msub><msub><mi>m</mi><mn>2</mn></msub></mrow><mrow><msup><mi>r</mi><mn>2</mn></msup></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
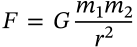
Escape Velocity
escape velocity
$$v_e = \sqrt{\frac{2GM}{r}}$$
v_e = \sqrt{\frac{2GM}{r}}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><msub><mi>v</mi><mi>e</mi></msub><mo>=</mo><msqrt><mrow><mfrac><mrow><mn>2</mn><mi>G</mi><mi>M</mi></mrow><mrow><mi>r</mi></mrow></mfrac></mrow></msqrt></mrow></math>
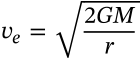
Kinetic Energy
kinetic energy motion
$$E = \frac{1}{2} mv^2$$
E = \frac{1}{2} mv^2
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>E</mi><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><mn>1</mn></mrow><mrow><mn>2</mn></mrow></mfrac><mi>m</mi><msup><mi>v</mi><mn>2</mn></msup></mrow></math>
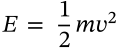
Work
work force motion
$$W = F \Delta r$$
W = F \Delta r
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>W</mi><mo>=</mo><mi>F</mi><mi>Δ</mi><mi>r</mi></mrow></math>
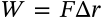
Work (general)
work (general) force motion
$$W = \int_C F(r) \cdot \mathrm{d}r$$
W = \int_C F(r) \cdot \mathrm{d}r
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>W</mi><mo>=</mo><msub><mo>∫</mo><mi>C</mi></msub><mi>F</mi><mo stretchy="false">(</mo><mi>r</mi><mo stretchy="false">)</mo><mi>·</mi><mi>d</mi><mi>r</mi></mrow></math>
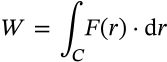
Momentum
momentum motion
$$p = mv$$
p = mv
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>p</mi><mo>=</mo><mi>m</mi><mi>v</mi></mrow></math>
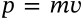
Momentum (special relativity)
momentum (special relativity) motion
$$p = \frac{mv}{\sqrt{1 - \frac{v^2}{c^2}}}$$
p = \frac{mv}{\sqrt{1 - \frac{v^2}{c^2}}}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>p</mi><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><mi>m</mi><mi>v</mi></mrow><mrow><msqrt><mrow><mn>1</mn><mo>−</mo><mfrac><mrow><msup><mi>v</mi><mn>2</mn></msup></mrow><mrow><msup><mi>c</mi><mn>2</mn></msup></mrow></mfrac></mrow></msqrt></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
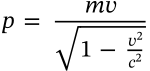
Density
density
$$\rho = \frac{m}{V}$$
\rho = \frac{m}{V}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>ρ</mi><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><mi>m</mi></mrow><mrow><mi>V</mi></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
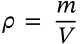
Pressure
pressure
$$p=\frac{F}{A}$$
p=\frac{F}{A}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>p</mi><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><mi>F</mi></mrow><mrow><mi>A</mi></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
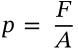
Moment of Inertia
moment of inertia
$$I = \frac{L}{\omega}$$
I = \frac{L}{\omega}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>I</mi><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><mi>L</mi></mrow><mrow><mi>ω</mi></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
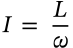
Torque
torque
$$\tau = rF\sin\theta$$
\tau = rF\sin\theta
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>τ</mi><mo>=</mo><mi>r</mi><mi>F</mi><mi>sin</mi><mi>θ</mi></mrow></math>
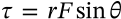
Centripetal Force
centripetal force
$$F_c = \frac{mv^2}{r}$$
F_c = \frac{mv^2}{r}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><msub><mi>F</mi><mi>c</mi></msub><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><mi>m</mi><msup><mi>v</mi><mn>2</mn></msup></mrow><mrow><mi>r</mi></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
Period of Pendulum
period of pendulum
$$T = 2\pi\sqrt{\frac{L}{g}}$$
T = 2\pi\sqrt{\frac{L}{g}}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>T</mi><mo>=</mo><mn>2</mn><mi>π</mi><msqrt><mrow><mfrac><mrow><mi>L</mi></mrow><mrow><mi>g</mi></mrow></mfrac></mrow></msqrt></mrow></math>
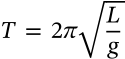
Period of Mass-Spring System
period of mass-spring system
$$T = 2\pi\sqrt{\frac{m}{k}}$$
T = 2\pi\sqrt{\frac{m}{k}}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>T</mi><mo>=</mo><mn>2</mn><mi>π</mi><msqrt><mrow><mfrac><mrow><mi>m</mi></mrow><mrow><mi>k</mi></mrow></mfrac></mrow></msqrt></mrow></math>
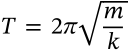
Energy in a Mass-Spring System
energy in a mass-spring system
$$E = \frac{1}{2}kx^2 + \frac{1}{2}mv^2 = \frac{1}{2}kA^2$$
E = \frac{1}{2}kx^2 + \frac{1}{2}mv^2 = \frac{1}{2}kA^2
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>E</mi><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><mn>1</mn></mrow><mrow><mn>2</mn></mrow></mfrac><mi>k</mi><msup><mi>x</mi><mn>2</mn></msup><mo>+</mo><mfrac><mrow><mn>1</mn></mrow><mrow><mn>2</mn></mrow></mfrac><mi>m</mi><msup><mi>v</mi><mn>2</mn></msup><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><mn>1</mn></mrow><mrow><mn>2</mn></mrow></mfrac><mi>k</mi><msup><mi>A</mi><mn>2</mn></msup></mrow></math>
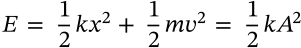
Velocity of Mass-Spring System
velocity of mass-spring system
$$v = \pm \sqrt{\frac{k}{m}(A^2 - x^2)}$$
v = \pm \sqrt{\frac{k}{m}(A^2 - x^2)}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>v</mi><mo>=</mo><mi>±</mi><msqrt><mrow><mfrac><mrow><mi>k</mi></mrow><mrow><mi>m</mi></mrow></mfrac><mo stretchy="false">(</mo><msup><mi>A</mi><mn>2</mn></msup><mo>−</mo><msup><mi>x</mi><mn>2</mn></msup><mo stretchy="false">)</mo></mrow></msqrt></mrow></math>
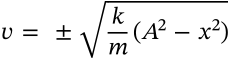
Hooke's Law (Spring Equation)
hooke's law (spring equation)
$$F = kx$$
F = kx
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>F</mi><mo>=</mo><mi>k</mi><mi>x</mi></mrow></math>
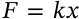
Fick's first law of diffusion
fick's first law of diffusion
$$J = -D\frac{d\varphi}{dx}$$
J = -D\frac{d\varphi}{dx}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>J</mi><mo>=</mo><mo>−</mo><mi>D</mi><mfrac><mrow><mi>d</mi><mi>φ</mi></mrow><mrow><mi>d</mi><mi>x</mi></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
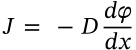
Fick's second law of diffusion
fick's second law of diffusion
$$\frac{\partial\varphi}{\partial t} = D\frac{\partial^2\varphi}{\partial x^2}$$
\frac{\partial\varphi}{\partial t} = D\frac{\partial^2\varphi}{\partial x^2}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mfrac><mrow><mo>∂</mo><mi>φ</mi></mrow><mrow><mo>∂</mo><mi>t</mi></mrow></mfrac><mo>=</mo><mi>D</mi><mfrac><mrow><msup><mo>∂</mo><mn>2</mn></msup><mi>φ</mi></mrow><mrow><mo>∂</mo><msup><mi>x</mi><mn>2</mn></msup></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
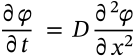
Diffusion Equation
diffusion equation
$$\frac{\partial \phi(r, t)}{\partial t} = \nabla \cdot [D(\phi,r) \, \nabla \phi(r, t)]$$
\frac{\partial \phi(r, t)}{\partial t} = \nabla \cdot [D(\phi,r) \, \nabla \phi(r, t)]
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mfrac><mrow><mo>∂</mo><mi>ϕ</mi><mo stretchy="false">(</mo><mi>r</mi><mo>,</mo><mi>t</mi><mo stretchy="false">)</mo></mrow><mrow><mo>∂</mo><mi>t</mi></mrow></mfrac><mo>=</mo><mo>∇</mo><mi>·</mi><mo stretchy="false">[</mo><mi>D</mi><mo stretchy="false">(</mo><mi>ϕ</mi><mo>,</mo><mi>r</mi><mo stretchy="false">)</mo><mspace width="0.167em" /><mo>∇</mo><mi>ϕ</mi><mo stretchy="false">(</mo><mi>r</mi><mo>,</mo><mi>t</mi><mo stretchy="false">)</mo><mo stretchy="false">]</mo></mrow></math>
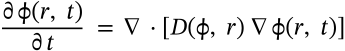
Heat Equation
heat equation
$$\frac{\partial u}{\partial t} = \Delta u$$
\frac{\partial u}{\partial t} = \Delta u
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mfrac><mrow><mo>∂</mo><mi>u</mi></mrow><mrow><mo>∂</mo><mi>t</mi></mrow></mfrac><mo>=</mo><mi>Δ</mi><mi>u</mi></mrow></math>
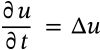
Thermal Conduction
thermal conduction
$$q = -k \nabla T$$
q = -k \nabla T
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>q</mi><mo>=</mo><mo>−</mo><mi>k</mi><mo>∇</mo><mi>T</mi></mrow></math>
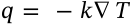
Ideal Gas Law
ideal gas law
$$PV = nRT$$
PV = nRT
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>P</mi><mi>V</mi><mo>=</mo><mi>n</mi><mi>R</mi><mi>T</mi></mrow></math>
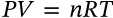
Boyle's Law
boyle's law boyle mariotte gas
$$P \propto \frac{1}{V}$$
P \propto \frac{1}{V}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>P</mi><mo>∝</mo><mfrac><mrow><mn>1</mn></mrow><mrow><mi>V</mi></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
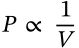
Charles's Law
charles's law
$$V \propto T$$
V \propto T
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>V</mi><mo>∝</mo><mi>T</mi></mrow></math>
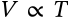
Avogadro's Law
avogadro's law
$$V \propto n$$
V \propto n
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>V</mi><mo>∝</mo><mi>n</mi></mrow></math>
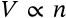
Molar Mass of a Gas
molar mass of a gas
$$M = \frac{RT\rho}{p}$$
M = \frac{RT\rho}{p}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>M</mi><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><mi>R</mi><mi>T</mi><mi>ρ</mi></mrow><mrow><mi>p</mi></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
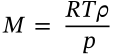
Navier-Stokes Equation
navier-stokes equation
$$\rho \cdot \left( \frac{\partial \vec{\mathbf{v}}}{\partial t} + \vec{\mathbf{v}} \cdot \nabla \vec{\mathbf{v}} \right) = \rho \vec{\mathbf{g}} - \nabla p + \mu \cdot \nabla^2 \vec{\mathbf{v}}$$
\rho \cdot \left( \frac{\partial \vec{\mathbf{v}}}{\partial t} + \vec{\mathbf{v}} \cdot \nabla \vec{\mathbf{v}} \right) = \rho \vec{\mathbf{g}} - \nabla p + \mu \cdot \nabla^2 \vec{\mathbf{v}}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>ρ</mi><mi>·</mi><mrow><mo stretchy="true" fence="true" form="prefix">(</mo><mfrac><mrow><mo>∂</mo><mover><mrow><mi>𝐯</mi></mrow><mo stretchy="true">→</mo></mover></mrow><mrow><mo>∂</mo><mi>t</mi></mrow></mfrac><mo>+</mo><mover><mrow><mi>𝐯</mi></mrow><mo stretchy="true">→</mo></mover><mi>·</mi><mo>∇</mo><mover><mrow><mi>𝐯</mi></mrow><mo stretchy="true">→</mo></mover><mo stretchy="true" fence="true" form="postfix">)</mo></mrow><mo>=</mo><mi>ρ</mi><mover><mrow><mi>𝐠</mi></mrow><mo stretchy="true">→</mo></mover><mo>−</mo><mo>∇</mo><mi>p</mi><mo>+</mo><mi>μ</mi><mi>·</mi><msup><mo>∇</mo><mn>2</mn></msup><mover><mrow><mi>𝐯</mi></mrow><mo stretchy="true">→</mo></mover></mrow></math>
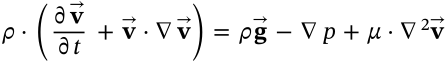
Bernoulli's Principle
bernoulli's principle
$$P_1 + \frac{1}{2}\rho v_1^2 + \rho g h_1 = P_2 + \frac{1}{2}\rho v_2^2 + \rho g h_2$$
P_1 + \frac{1}{2}\rho v_1^2 + \rho g h_1 = P_2 + \frac{1}{2}\rho v_2^2 + \rho g h_2
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><msub><mi>P</mi><mn>1</mn></msub><mo>+</mo><mfrac><mrow><mn>1</mn></mrow><mrow><mn>2</mn></mrow></mfrac><mi>ρ</mi><msubsup><mi>v</mi><mn>1</mn><mn>2</mn></msubsup><mo>+</mo><mi>ρ</mi><mi>g</mi><msub><mi>h</mi><mn>1</mn></msub><mo>=</mo><msub><mi>P</mi><mn>2</mn></msub><mo>+</mo><mfrac><mrow><mn>1</mn></mrow><mrow><mn>2</mn></mrow></mfrac><mi>ρ</mi><msubsup><mi>v</mi><mn>2</mn><mn>2</mn></msubsup><mo>+</mo><mi>ρ</mi><mi>g</mi><msub><mi>h</mi><mn>2</mn></msub></mrow></math>
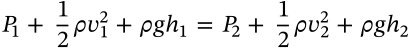
Van der Waals Equation
van der waals equation
$$(P + \frac{an^2}{V^2})(V - nb) = nRT$$
(P + \frac{an^2}{V^2})(V - nb) = nRT
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mo stretchy="false">(</mo><mi>P</mi><mo>+</mo><mfrac><mrow><mi>a</mi><msup><mi>n</mi><mn>2</mn></msup></mrow><mrow><msup><mi>V</mi><mn>2</mn></msup></mrow></mfrac><mo stretchy="false">)</mo><mo stretchy="false">(</mo><mi>V</mi><mo>−</mo><mi>n</mi><mi>b</mi><mo stretchy="false">)</mo><mo>=</mo><mi>n</mi><mi>R</mi><mi>T</mi></mrow></math>
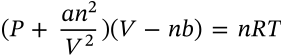
Dalton's Law
dalton's law
$$p_{total} = \sum_{i=1}^n p_i = p_1 + p_2 + p_3 + \cdots + p_n$$
p_{total} = \sum_{i=1}^n p_i = p_1 + p_2 + p_3 + \cdots + p_n
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><msub><mi>p</mi><mrow><mi>t</mi><mi>o</mi><mi>t</mi><mi>a</mi><mi>l</mi></mrow></msub><mo>=</mo><msubsup><mo>∑</mo><mrow><mi>i</mi><mo>=</mo><mn>1</mn></mrow><mi>n</mi></msubsup><msub><mi>p</mi><mi>i</mi></msub><mo>=</mo><msub><mi>p</mi><mn>1</mn></msub><mo>+</mo><msub><mi>p</mi><mn>2</mn></msub><mo>+</mo><msub><mi>p</mi><mn>3</mn></msub><mo>+</mo><mo>⋯</mo><mo>+</mo><msub><mi>p</mi><mi>n</mi></msub></mrow></math>
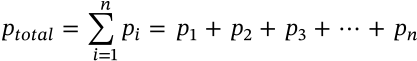
Amagat's Law
amagat's law
$$V_{mix} = \sum_{i=1}^k V_i = V_1 + V_2 + V_3 + \cdots + V_n$$
V_{mix} = \sum_{i=1}^k V_i = V_1 + V_2 + V_3 + \cdots + V_n
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><msub><mi>V</mi><mrow><mi>m</mi><mi>i</mi><mi>x</mi></mrow></msub><mo>=</mo><msubsup><mo>∑</mo><mrow><mi>i</mi><mo>=</mo><mn>1</mn></mrow><mi>k</mi></msubsup><msub><mi>V</mi><mi>i</mi></msub><mo>=</mo><msub><mi>V</mi><mn>1</mn></msub><mo>+</mo><msub><mi>V</mi><mn>2</mn></msub><mo>+</mo><msub><mi>V</mi><mn>3</mn></msub><mo>+</mo><mo>⋯</mo><mo>+</mo><msub><mi>V</mi><mi>n</mi></msub></mrow></math>
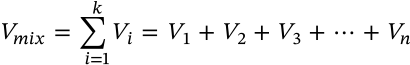
First Law of Thermodynamics
first law of thermodynamics
$$\Delta U = Q - W$$
\Delta U = Q - W
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>Δ</mi><mi>U</mi><mo>=</mo><mi>Q</mi><mo>−</mo><mi>W</mi></mrow></math>
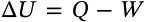
pH of a Solution
ph of a solution
$$\mathrm{pH} = -\log [H^+]$$
\mathrm{pH} = -\log [H^+]
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mrow><mi mathvariant="normal">p</mi><mi mathvariant="normal">H</mi></mrow><mo>=</mo><mo>−</mo><mi>log</mi><mo stretchy="false">[</mo><msup><mi>H</mi><mo>+</mo></msup><mo stretchy="false">]</mo></mrow></math>
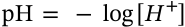
Nernst Equation
nernst equation
$$E = E^0 - \frac{RT}{zF}\ln{Q}$$
E = E^0 - \frac{RT}{zF}\ln{Q}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>E</mi><mo>=</mo><msup><mi>E</mi><mn>0</mn></msup><mo>−</mo><mfrac><mrow><mi>R</mi><mi>T</mi></mrow><mrow><mi>z</mi><mi>F</mi></mrow></mfrac><mi>ln</mi><mrow><mi>Q</mi></mrow></mrow></math>
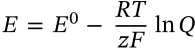
Law of Mass Action
law of mass action
$$K = \frac{[A']^{\alpha '}[B']^{\beta '} \cdots}{[A]^\alpha [B]^\beta \cdots}$$
K = \frac{[A']^{\alpha '}[B']^{\beta '} \cdots}{[A]^\alpha [B]^\beta \cdots}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>K</mi><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><mo stretchy="false">[</mo><msup><mi>A</mi><mi>′</mi></msup><msup><mo stretchy="false">]</mo><mrow><msup><mi>α</mi><mi>′</mi></msup></mrow></msup><mo stretchy="false">[</mo><msup><mi>B</mi><mi>′</mi></msup><msup><mo stretchy="false">]</mo><mrow><msup><mi>β</mi><mi>′</mi></msup></mrow></msup><mo>⋯</mo></mrow><mrow><mo stretchy="false">[</mo><mi>A</mi><msup><mo stretchy="false">]</mo><mi>α</mi></msup><mo stretchy="false">[</mo><mi>B</mi><msup><mo stretchy="false">]</mo><mi>β</mi></msup><mo>⋯</mo></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
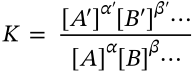
Arrhenius Equation
arrhenius equation
$$k = Ae^{-\frac{E_a}{RT}}$$
k = Ae^{-\frac{E_a}{RT}}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>k</mi><mo>=</mo><mi>A</mi><msup><mi>e</mi><mrow><mo>−</mo><mfrac><mrow><msub><mi>E</mi><mi>a</mi></msub></mrow><mrow><mi>R</mi><mi>T</mi></mrow></mfrac></mrow></msup></mrow></math>
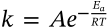
Raoult's Law
raoult's law
$$p_i = p_i^\star x_i$$
p_i = p_i^\star x_i
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><msub><mi>p</mi><mi>i</mi></msub><mo>=</mo><msubsup><mi>p</mi><mi>i</mi><mo>⋆</mo></msubsup><msub><mi>x</mi><mi>i</mi></msub></mrow></math>
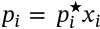
Köhler Equation
köhler equation kohler
$$\ln\left(\frac{p_w(D_p)}{p^0}\right) = \frac{4M_w \sigma_w}{RT\rho_w D_p} - \frac{6n_s M_w}{\pi\rho D_p^3}$$
\ln\left(\frac{p_w(D_p)}{p^0}\right) = \frac{4M_w \sigma_w}{RT\rho_w D_p} - \frac{6n_s M_w}{\pi\rho D_p^3}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>ln</mi><mrow><mo stretchy="true" fence="true" form="prefix">(</mo><mfrac><mrow><msub><mi>p</mi><mi>w</mi></msub><mo stretchy="false">(</mo><msub><mi>D</mi><mi>p</mi></msub><mo stretchy="false">)</mo></mrow><mrow><msup><mi>p</mi><mn>0</mn></msup></mrow></mfrac><mo stretchy="true" fence="true" form="postfix">)</mo></mrow><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><mn>4</mn><msub><mi>M</mi><mi>w</mi></msub><msub><mi>σ</mi><mi>w</mi></msub></mrow><mrow><mi>R</mi><mi>T</mi><msub><mi>ρ</mi><mi>w</mi></msub><msub><mi>D</mi><mi>p</mi></msub></mrow></mfrac><mo>−</mo><mfrac><mrow><mn>6</mn><msub><mi>n</mi><mi>s</mi></msub><msub><mi>M</mi><mi>w</mi></msub></mrow><mrow><mi>π</mi><mi>ρ</mi><msubsup><mi>D</mi><mi>p</mi><mn>3</mn></msubsup></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
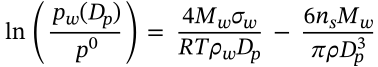
Kelvin Equation
kelvin equation
$$p(r_1,r_2) = P - \frac{\gamma \rho_{\mathrm{vapor}}}{\rho_{\mathrm{liquid}} - \rho_{\mathrm{vapor}}} \left(\frac{1}{r_1} + \frac{1}{r_2}\right)$$
p(r_1,r_2) = P - \frac{\gamma \rho_{\mathrm{vapor}}}{\rho_{\mathrm{liquid}} - \rho_{\mathrm{vapor}}} \left(\frac{1}{r_1} + \frac{1}{r_2}\right)
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>p</mi><mo stretchy="false">(</mo><msub><mi>r</mi><mn>1</mn></msub><mo>,</mo><msub><mi>r</mi><mn>2</mn></msub><mo stretchy="false">)</mo><mo>=</mo><mi>P</mi><mo>−</mo><mfrac><mrow><mi>γ</mi><msub><mi>ρ</mi><mrow><mrow><mi mathvariant="normal">v</mi><mi mathvariant="normal">a</mi><mi mathvariant="normal">p</mi><mi mathvariant="normal">o</mi><mi mathvariant="normal">r</mi></mrow></mrow></msub></mrow><mrow><msub><mi>ρ</mi><mrow><mrow><mi mathvariant="normal">l</mi><mi mathvariant="normal">i</mi><mi mathvariant="normal">q</mi><mi mathvariant="normal">u</mi><mi mathvariant="normal">i</mi><mi mathvariant="normal">d</mi></mrow></mrow></msub><mo>−</mo><msub><mi>ρ</mi><mrow><mrow><mi mathvariant="normal">v</mi><mi mathvariant="normal">a</mi><mi mathvariant="normal">p</mi><mi mathvariant="normal">o</mi><mi mathvariant="normal">r</mi></mrow></mrow></msub></mrow></mfrac><mrow><mo stretchy="true" fence="true" form="prefix">(</mo><mfrac><mrow><mn>1</mn></mrow><mrow><msub><mi>r</mi><mn>1</mn></msub></mrow></mfrac><mo>+</mo><mfrac><mrow><mn>1</mn></mrow><mrow><msub><mi>r</mi><mn>2</mn></msub></mrow></mfrac><mo stretchy="true" fence="true" form="postfix">)</mo></mrow></mrow></math>
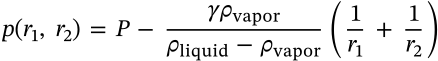
Ostwald-Freundlich Equation
ostwald-freundlich equation
$$\ln{\frac{p}{p_{sat}}} = \frac{2\gamma V_m}{rRT}$$
\ln{\frac{p}{p_{sat}}} = \frac{2\gamma V_m}{rRT}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>ln</mi><mrow><mfrac><mrow><mi>p</mi></mrow><mrow><msub><mi>p</mi><mrow><mi>s</mi><mi>a</mi><mi>t</mi></mrow></msub></mrow></mfrac></mrow><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><mn>2</mn><mi>γ</mi><msub><mi>V</mi><mi>m</mi></msub></mrow><mrow><mi>r</mi><mi>R</mi><mi>T</mi></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
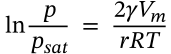
Standing Wave Equation
standing wave equation
$$y(x, y) = A_n \cos(\omega_n t + \delta_n) \sin(k_n x)$$
y(x, y) = A_n \cos(\omega_n t + \delta_n) \sin(k_n x)
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>y</mi><mo stretchy="false">(</mo><mi>x</mi><mo>,</mo><mi>y</mi><mo stretchy="false">)</mo><mo>=</mo><msub><mi>A</mi><mi>n</mi></msub><mi>cos</mi><mo stretchy="false">(</mo><msub><mi>ω</mi><mi>n</mi></msub><mi>t</mi><mo>+</mo><msub><mi>δ</mi><mi>n</mi></msub><mo stretchy="false">)</mo><mi>sin</mi><mo stretchy="false">(</mo><msub><mi>k</mi><mi>n</mi></msub><mi>x</mi><mo stretchy="false">)</mo></mrow></math>
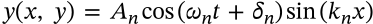
Stefan-Boltzmann Law
stefan-boltzmann law
$$j^\star = \sigma T^4$$
j^\star = \sigma T^4
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><msup><mi>j</mi><mo>⋆</mo></msup><mo>=</mo><mi>σ</mi><msup><mi>T</mi><mn>4</mn></msup></mrow></math>
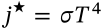
Stefan-Boltzmann Constant
stefan-boltzmann constant
$$\sigma = \frac{2\pi^5 k^4}{15 c^2 h^3}$$
\sigma = \frac{2\pi^5 k^4}{15 c^2 h^3}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>σ</mi><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><mn>2</mn><msup><mi>π</mi><mn>5</mn></msup><msup><mi>k</mi><mn>4</mn></msup></mrow><mrow><mn>15</mn><msup><mi>c</mi><mn>2</mn></msup><msup><mi>h</mi><mn>3</mn></msup></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
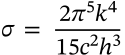
Tsiolkovsky Rocket Equation
tsiolkovsky rocket equation ideal rocket equation
$$\Delta v = v_e \ln{\frac{m_0}{m_f}} = I_{sp} g_0 \ln{\frac{m_0}{m_f}}$$
\Delta v = v_e \ln{\frac{m_0}{m_f}} = I_{sp} g_0 \ln{\frac{m_0}{m_f}}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>Δ</mi><mi>v</mi><mo>=</mo><msub><mi>v</mi><mi>e</mi></msub><mi>ln</mi><mrow><mfrac><mrow><msub><mi>m</mi><mn>0</mn></msub></mrow><mrow><msub><mi>m</mi><mi>f</mi></msub></mrow></mfrac></mrow><mo>=</mo><msub><mi>I</mi><mrow><mi>s</mi><mi>p</mi></mrow></msub><msub><mi>g</mi><mn>0</mn></msub><mi>ln</mi><mrow><mfrac><mrow><msub><mi>m</mi><mn>0</mn></msub></mrow><mrow><msub><mi>m</mi><mi>f</mi></msub></mrow></mfrac></mrow></mrow></math>
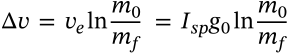
Methane Combustion
methane combustion
$$\mathrm{1 CH_4 + O_2 \to CO_2 + H_2O}$$
\mathrm{1 CH_4 + O_2 \to CO_2 + H_2O}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mrow><mn>1</mn><mi mathvariant="normal">C</mi><msub><mi mathvariant="normal">H</mi><mn>4</mn></msub><mo>+</mo><msub><mi mathvariant="normal">O</mi><mn>2</mn></msub><mo>→</mo><mi mathvariant="normal">C</mi><msub><mi mathvariant="normal">O</mi><mn>2</mn></msub><mo>+</mo><msub><mi mathvariant="normal">H</mi><mn>2</mn></msub><mi mathvariant="normal">O</mi></mrow></mrow></math>

Photosynthesis
photosynthesis
$$\mathrm{6CO_2 + 6H_2O \to C_6 H_{12} O_6 + 6O_2}$$
\mathrm{6CO_2 + 6H_2O \to C_6 H_{12} O_6 + 6O_2}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mrow><mn>6</mn><mi mathvariant="normal">C</mi><msub><mi mathvariant="normal">O</mi><mn>2</mn></msub><mo>+</mo><mn>6</mn><msub><mi mathvariant="normal">H</mi><mn>2</mn></msub><mi mathvariant="normal">O</mi><mo>→</mo><msub><mi mathvariant="normal">C</mi><mn>6</mn></msub><msub><mi mathvariant="normal">H</mi><mrow><mn>12</mn></mrow></msub><msub><mi mathvariant="normal">O</mi><mn>6</mn></msub><mo>+</mo><mn>6</mn><msub><mi mathvariant="normal">O</mi><mn>2</mn></msub></mrow></mrow></math>
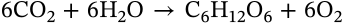
Speed of Sound
speed of sound
$$v = \sqrt{\frac{K_s}{\rho}}$$
v = \sqrt{\frac{K_s}{\rho}}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>v</mi><mo>=</mo><msqrt><mrow><mfrac><mrow><msub><mi>K</mi><mi>s</mi></msub></mrow><mrow><mi>ρ</mi></mrow></mfrac></mrow></msqrt></mrow></math>
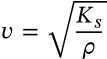
Doppler Effect
doppler effect
$$f_o = \frac{v + v_o}{v + v_s} f_s$$
f_o = \frac{v + v_o}{v + v_s} f_s
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><msub><mi>f</mi><mi>o</mi></msub><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><mi>v</mi><mo>+</mo><msub><mi>v</mi><mi>o</mi></msub></mrow><mrow><mi>v</mi><mo>+</mo><msub><mi>v</mi><mi>s</mi></msub></mrow></mfrac><msub><mi>f</mi><mi>s</mi></msub></mrow></math>
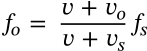
Hagen-Poiseuille Equation
hagen-poiseuille equation
$$\delta p = \frac{8 \mu L Q}{\pi R^4}$$
\delta p = \frac{8 \mu L Q}{\pi R^4}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>δ</mi><mi>p</mi><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><mn>8</mn><mi>μ</mi><mi>L</mi><mi>Q</mi></mrow><mrow><mi>π</mi><msup><mi>R</mi><mn>4</mn></msup></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
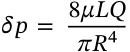
Continuity Equation
continuity equation
$$A_1 v_1 = A_2 v_2$$
A_1 v_1 = A_2 v_2
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><msub><mi>A</mi><mn>1</mn></msub><msub><mi>v</mi><mn>1</mn></msub><mo>=</mo><msub><mi>A</mi><mn>2</mn></msub><msub><mi>v</mi><mn>2</mn></msub></mrow></math>
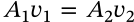
Viscosity
viscosity
$$\eta = \frac{FL}{vA}$$
\eta = \frac{FL}{vA}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>η</mi><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><mi>F</mi><mi>L</mi></mrow><mrow><mi>v</mi><mi>A</mi></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
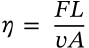
Kirchoff's Current Law
kirchoff's current law
$$\sum_{k=1}^n I_k = 0$$
\sum_{k=1}^n I_k = 0
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><msubsup><mo>∑</mo><mrow><mi>k</mi><mo>=</mo><mn>1</mn></mrow><mi>n</mi></msubsup><msub><mi>I</mi><mi>k</mi></msub><mo>=</mo><mn>0</mn></mrow></math>
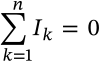
Kirchoff's Voltage Law
kirchoff's voltage law
$$\sum_{k=1}^n V_k = 0$$
\sum_{k=1}^n V_k = 0
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><msubsup><mo>∑</mo><mrow><mi>k</mi><mo>=</mo><mn>1</mn></mrow><mi>n</mi></msubsup><msub><mi>V</mi><mi>k</mi></msub><mo>=</mo><mn>0</mn></mrow></math>
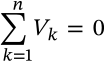
Gauss's Law
gauss's law maxwell
$$\nabla \cdot E = \rho_v/\epsilon$$
\nabla \cdot E = \rho_v/\epsilon
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mo>∇</mo><mi>·</mi><mi>E</mi><mo>=</mo><msub><mi>ρ</mi><mi>v</mi></msub><mo>/</mo><mi>ϵ</mi></mrow></math>
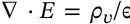
Gauss's Magnetism Law
gauss's magnetism law maxwell
$$\nabla \cdot B = 0$$
\nabla \cdot B = 0
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mo>∇</mo><mi>·</mi><mi>B</mi><mo>=</mo><mn>0</mn></mrow></math>
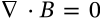
Faraday's Law
faraday's law maxwell
$$\nabla \times E = -\frac{\partial B}{\partial t}$$
\nabla \times E = -\frac{\partial B}{\partial t}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mo>∇</mo><mi>×</mi><mi>E</mi><mo>=</mo><mo>−</mo><mfrac><mrow><mo>∂</mo><mi>B</mi></mrow><mrow><mo>∂</mo><mi>t</mi></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
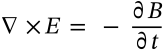
Ampere's Law
ampere's law maxwell
$$\nabla \times B = \mu_0 J + \mu_0\epsilon_0 \frac{\partial E}{\partial t}$$
\nabla \times B = \mu_0 J + \mu_0\epsilon_0 \frac{\partial E}{\partial t}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mo>∇</mo><mi>×</mi><mi>B</mi><mo>=</mo><msub><mi>μ</mi><mn>0</mn></msub><mi>J</mi><mo>+</mo><msub><mi>μ</mi><mn>0</mn></msub><msub><mi>ϵ</mi><mn>0</mn></msub><mfrac><mrow><mo>∂</mo><mi>E</mi></mrow><mrow><mo>∂</mo><mi>t</mi></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
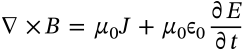
Gauss's Law (Integral Form)
gauss's law (integral form) maxwell
$$\oiint_S E \cdot dA = \frac{Q}{\epsilon_0}$$
\oiint_S E \cdot dA = \frac{Q}{\epsilon_0}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><msub><mo>∯</mo><mi>S</mi></msub><mi>E</mi><mi>·</mi><mi>d</mi><mi>A</mi><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><mi>Q</mi></mrow><mrow><msub><mi>ϵ</mi><mn>0</mn></msub></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
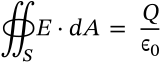
Gauss's Magnetism Law (Integral Form)
gauss's magnetism law (integral form) maxwell
$$\oiint_S B \cdot dS = 0$$
\oiint_S B \cdot dS = 0
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><msub><mo>∯</mo><mi>S</mi></msub><mi>B</mi><mi>·</mi><mi>d</mi><mi>S</mi><mo>=</mo><mn>0</mn></mrow></math>
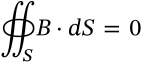
Faraday's Law (Integral Form)
faraday's law (integral form) maxwell
$$\oint_{\partial S} E \cdot dl = -\int_S \frac{\partial B}{\partial t} \cdot dA$$
\oint_{\partial S} E \cdot dl = -\int_S \frac{\partial B}{\partial t} \cdot dA
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><msub><mo>∮</mo><mrow><mo>∂</mo><mi>S</mi></mrow></msub><mi>E</mi><mi>·</mi><mi>d</mi><mi>l</mi><mo>=</mo><mo>−</mo><msub><mo>∫</mo><mi>S</mi></msub><mfrac><mrow><mo>∂</mo><mi>B</mi></mrow><mrow><mo>∂</mo><mi>t</mi></mrow></mfrac><mi>·</mi><mi>d</mi><mi>A</mi></mrow></math>
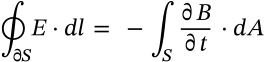
Ampere's Law (Integral Form)
ampere's law (integral form) maxwell
$$\oint_C B \cdot dl = \iint_S \left(\mu_0 J + \mu_0 \epsilon_0 \frac{\partial E}{\partial t}\right) \cdot dS$$
\oint_C B \cdot dl = \iint_S \left(\mu_0 J + \mu_0 \epsilon_0 \frac{\partial E}{\partial t}\right) \cdot dS
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><msub><mo>∮</mo><mi>C</mi></msub><mi>B</mi><mi>·</mi><mi>d</mi><mi>l</mi><mo>=</mo><msub><mo>∬</mo><mi>S</mi></msub><mrow><mo stretchy="true" fence="true" form="prefix">(</mo><msub><mi>μ</mi><mn>0</mn></msub><mi>J</mi><mo>+</mo><msub><mi>μ</mi><mn>0</mn></msub><msub><mi>ϵ</mi><mn>0</mn></msub><mfrac><mrow><mo>∂</mo><mi>E</mi></mrow><mrow><mo>∂</mo><mi>t</mi></mrow></mfrac><mo stretchy="true" fence="true" form="postfix">)</mo></mrow><mi>·</mi><mi>d</mi><mi>S</mi></mrow></math>
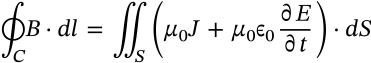
Coulomb's Law
coulomb's law
$$|F| = K\frac{|q_1 q_2|}{r^2}$$
|F| = K\frac{|q_1 q_2|}{r^2}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mo stretchy="false">|</mo><mi>F</mi><mo stretchy="false">|</mo><mo>=</mo><mi>K</mi><mfrac><mrow><mo stretchy="false">|</mo><msub><mi>q</mi><mn>1</mn></msub><msub><mi>q</mi><mn>2</mn></msub><mo stretchy="false">|</mo></mrow><mrow><msup><mi>r</mi><mn>2</mn></msup></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
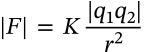
Lorentz Force
lorentz force
$$F = qE + qv \times B$$
F = qE + qv \times B
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>F</mi><mo>=</mo><mi>q</mi><mi>E</mi><mo>+</mo><mi>q</mi><mi>v</mi><mi>×</mi><mi>B</mi></mrow></math>
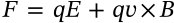
Current
current ampere charge
$$I = \frac{\Delta q}{\Delta t}$$
I = \frac{\Delta q}{\Delta t}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>I</mi><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><mi>Δ</mi><mi>q</mi></mrow><mrow><mi>Δ</mi><mi>t</mi></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
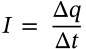
Resistance
resistance resistivity
$$R = \frac{\rho L}{A}$$
R = \frac{\rho L}{A}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>R</mi><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><mi>ρ</mi><mi>L</mi></mrow><mrow><mi>A</mi></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
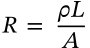
Conductivity
conductivity resistivity
$$\sigma = \frac{1}{\rho}$$
\sigma = \frac{1}{\rho}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>σ</mi><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><mn>1</mn></mrow><mrow><mi>ρ</mi></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
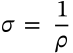
Ohm's Law
ohm's law ohms voltage current ampere resistance
$$V = IR$$
V = IR
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>V</mi><mo>=</mo><mi>I</mi><mi>R</mi></mrow></math>
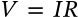
Power
power watt joule volt current
$$P = VI = \frac{V^2}{R} = I^2 R$$
P = VI = \frac{V^2}{R} = I^2 R
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>P</mi><mo>=</mo><mi>V</mi><mi>I</mi><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><msup><mi>V</mi><mn>2</mn></msup></mrow><mrow><mi>R</mi></mrow></mfrac><mo>=</mo><msup><mi>I</mi><mn>2</mn></msup><mi>R</mi></mrow></math>
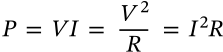
Series Resistors
series resistors
$$R = \sum_{i=1}^n R_i$$
R = \sum_{i=1}^n R_i
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>R</mi><mo>=</mo><msubsup><mo>∑</mo><mrow><mi>i</mi><mo>=</mo><mn>1</mn></mrow><mi>n</mi></msubsup><msub><mi>R</mi><mi>i</mi></msub></mrow></math>
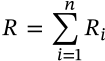
Parallel Resistors
parallel resistors
$$\frac{1}{R} = \sum_{i=1}^n \frac{1}{R_i}$$
\frac{1}{R} = \sum_{i=1}^n \frac{1}{R_i}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mfrac><mrow><mn>1</mn></mrow><mrow><mi>R</mi></mrow></mfrac><mo>=</mo><msubsup><mo>∑</mo><mrow><mi>i</mi><mo>=</mo><mn>1</mn></mrow><mi>n</mi></msubsup><mfrac><mrow><mn>1</mn></mrow><mrow><msub><mi>R</mi><mi>i</mi></msub></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
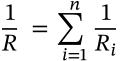
Capacitance Charge
capacitance charge
$$C = \frac{Q}{V}$$
C = \frac{Q}{V}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>C</mi><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><mi>Q</mi></mrow><mrow><mi>V</mi></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
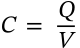
Parallel Plate Capacitor
parallel plate capacitor permittivity
$$C = \frac{\epsilon A}{d}$$
C = \frac{\epsilon A}{d}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>C</mi><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><mi>ϵ</mi><mi>A</mi></mrow><mrow><mi>d</mi></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
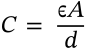
Capacitor Voltage
capacitor voltage
$$v = \frac{1}{C} \int_0^T i \mathrm{d}t + v_0$$
v = \frac{1}{C} \int_0^T i \mathrm{d}t + v_0
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>v</mi><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><mn>1</mn></mrow><mrow><mi>C</mi></mrow></mfrac><msubsup><mo>∫</mo><mn>0</mn><mi>T</mi></msubsup><mi>i</mi><mi>d</mi><mi>t</mi><mo>+</mo><msub><mi>v</mi><mn>0</mn></msub></mrow></math>
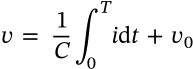
Capacitor Current
capacitor current
$$i = C \frac{\mathrm{d}v}{\mathrm{d}t}$$
i = C \frac{\mathrm{d}v}{\mathrm{d}t}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>i</mi><mo>=</mo><mi>C</mi><mfrac><mrow><mi>d</mi><mi>v</mi></mrow><mrow><mi>d</mi><mi>t</mi></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
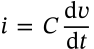
Capacitor Stored Energy
capacitor stored energy
$$W = \frac{1}{2}C V^2$$
W = \frac{1}{2}C V^2
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>W</mi><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><mn>1</mn></mrow><mrow><mn>2</mn></mrow></mfrac><mi>C</mi><msup><mi>V</mi><mn>2</mn></msup></mrow></math>
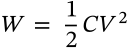
Inductor Voltage
inductor voltage
$$v = L \frac{\mathrm{d}i}{\mathrm{d}t}$$
v = L \frac{\mathrm{d}i}{\mathrm{d}t}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>v</mi><mo>=</mo><mi>L</mi><mfrac><mrow><mi>d</mi><mi>i</mi></mrow><mrow><mi>d</mi><mi>t</mi></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
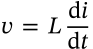
Inductor Current
inductor current
$$v = \frac{1}{L} \int_0^T v \mathrm{d}t + i_0$$
v = \frac{1}{L} \int_0^T v \mathrm{d}t + i_0
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>v</mi><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><mn>1</mn></mrow><mrow><mi>L</mi></mrow></mfrac><msubsup><mo>∫</mo><mn>0</mn><mi>T</mi></msubsup><mi>v</mi><mi>d</mi><mi>t</mi><mo>+</mo><msub><mi>i</mi><mn>0</mn></msub></mrow></math>
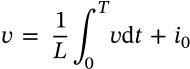
Inductor Stored Energy
inductor stored energy
$$W = \frac{1}{2}L I_0^2$$
W = \frac{1}{2}L I_0^2
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>W</mi><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><mn>1</mn></mrow><mrow><mn>2</mn></mrow></mfrac><mi>L</mi><msubsup><mi>I</mi><mn>0</mn><mn>2</mn></msubsup></mrow></math>
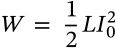
Shockley Diode Equation
shockley diode equation
$$I = I_s \left( e^{\frac{V_D}{nV_T}} - 1\right)$$
I = I_s \left( e^{\frac{V_D}{nV_T}} - 1\right)
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>I</mi><mo>=</mo><msub><mi>I</mi><mi>s</mi></msub><mrow><mo stretchy="true" fence="true" form="prefix">(</mo><msup><mi>e</mi><mrow><mfrac><mrow><msub><mi>V</mi><mi>D</mi></msub></mrow><mrow><mi>n</mi><msub><mi>V</mi><mi>T</mi></msub></mrow></mfrac></mrow></msup><mo>−</mo><mn>1</mn><mo stretchy="true" fence="true" form="postfix">)</mo></mrow></mrow></math>
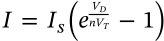
Fermi-Dirac Distribution
fermi-dirac distribution
$$n_i = \frac{1}{e^{(\epsilon_i - \mu)/k_B T} + 1}$$
n_i = \frac{1}{e^{(\epsilon_i - \mu)/k_B T} + 1}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><msub><mi>n</mi><mi>i</mi></msub><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><mn>1</mn></mrow><mrow><msup><mi>e</mi><mrow><mo stretchy="false">(</mo><msub><mi>ϵ</mi><mi>i</mi></msub><mo>−</mo><mi>μ</mi><mo stretchy="false">)</mo><mo>/</mo><msub><mi>k</mi><mi>B</mi></msub><mi>T</mi></mrow></msup><mo>+</mo><mn>1</mn></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
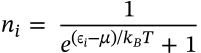
Frequency and Period
frequency and period
$$f = \frac{1}{T}$$
f = \frac{1}{T}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>f</mi><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><mn>1</mn></mrow><mrow><mi>T</mi></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
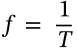
Wavelength
wavelength frequency
$$\lambda = \frac{v}{f}$$
\lambda = \frac{v}{f}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>λ</mi><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><mi>v</mi></mrow><mrow><mi>f</mi></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
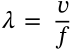
Photon Energy
photon energy
$$E = h\nu$$
E = h\nu
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>E</mi><mo>=</mo><mi>h</mi><mi>ν</mi></mrow></math>
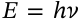
Wave Equation
wave equation
$$\frac{\partial^2 u}{\partial t^2} = c^2 \frac{\partial^2 u}{\partial x^2}$$
\frac{\partial^2 u}{\partial t^2} = c^2 \frac{\partial^2 u}{\partial x^2}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mfrac><mrow><msup><mo>∂</mo><mn>2</mn></msup><mi>u</mi></mrow><mrow><mo>∂</mo><msup><mi>t</mi><mn>2</mn></msup></mrow></mfrac><mo>=</mo><msup><mi>c</mi><mn>2</mn></msup><mfrac><mrow><msup><mo>∂</mo><mn>2</mn></msup><mi>u</mi></mrow><mrow><mo>∂</mo><msup><mi>x</mi><mn>2</mn></msup></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
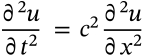
General Relativity
general relativity einstein
$$G_{\alpha \beta} = \frac{8\pi G}{c^4} T_{\alpha\beta}$$
G_{\alpha \beta} = \frac{8\pi G}{c^4} T_{\alpha\beta}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><msub><mi>G</mi><mrow><mi>α</mi><mi>β</mi></mrow></msub><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><mn>8</mn><mi>π</mi><mi>G</mi></mrow><mrow><msup><mi>c</mi><mn>4</mn></msup></mrow></mfrac><msub><mi>T</mi><mrow><mi>α</mi><mi>β</mi></mrow></msub></mrow></math>
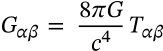
Schrödinger Equation
schrödinger equation schrodinger wave
$$i \hbar \frac{\partial}{\partial t}\Psi(\mathbf{r},t) = \hat H \Psi(\mathbf{r},t)$$
i \hbar \frac{\partial}{\partial t}\Psi(\mathbf{r},t) = \hat H \Psi(\mathbf{r},t)
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>i</mi><mi>ℏ</mi><mfrac><mrow><mo>∂</mo></mrow><mrow><mo>∂</mo><mi>t</mi></mrow></mfrac><mi>Ψ</mi><mo stretchy="false">(</mo><mi>𝐫</mi><mo>,</mo><mi>t</mi><mo stretchy="false">)</mo><mo>=</mo><mover><mi>H</mi><mo stretchy="false">^</mo></mover><mi>Ψ</mi><mo stretchy="false">(</mo><mi>𝐫</mi><mo>,</mo><mi>t</mi><mo stretchy="false">)</mo></mrow></math>
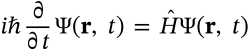
Mass-Energy Equivalence
mass-energy equivalence einstein
$$E = mc^2$$
E = mc^2
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>E</mi><mo>=</mo><mi>m</mi><msup><mi>c</mi><mn>2</mn></msup></mrow></math>
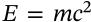
Rydberg Constant
rydberg constant
$$R_\infty = \frac{m_e e^4}{8 \epsilon_0^2 h^3 c}$$
R_\infty = \frac{m_e e^4}{8 \epsilon_0^2 h^3 c}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><msub><mi>R</mi><mo>∞</mo></msub><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><msub><mi>m</mi><mi>e</mi></msub><msup><mi>e</mi><mn>4</mn></msup></mrow><mrow><mn>8</mn><msubsup><mi>ϵ</mi><mn>0</mn><mn>2</mn></msubsup><msup><mi>h</mi><mn>3</mn></msup><mi>c</mi></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
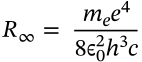
Bohr radius
bohr radius
$$a_0 = \frac{4 \pi \epsilon_0 \hbar^2}{m_e e^2}$$
a_0 = \frac{4 \pi \epsilon_0 \hbar^2}{m_e e^2}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><msub><mi>a</mi><mn>0</mn></msub><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><mn>4</mn><mi>π</mi><msub><mi>ϵ</mi><mn>0</mn></msub><msup><mi>ℏ</mi><mn>2</mn></msup></mrow><mrow><msub><mi>m</mi><mi>e</mi></msub><msup><mi>e</mi><mn>2</mn></msup></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>
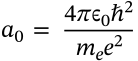
Planck Relation
planck relation
$$E = hv = \hbar\omega$$
E = hv = \hbar\omega
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>E</mi><mo>=</mo><mi>h</mi><mi>v</mi><mo>=</mo><mi>ℏ</mi><mi>ω</mi></mrow></math>
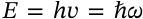
de Broglie Relation
de broglie relation
$$p = \hbar k$$
p = \hbar k
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>p</mi><mo>=</mo><mi>ℏ</mi><mi>k</mi></mrow></math>
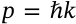
Planck's Law
planck's law
$$B(v, T) = \frac{2 h v^3}{c^2} \frac{1}{\exp\left(\frac{hv}{k_B T}\right) - 1}$$
B(v, T) = \frac{2 h v^3}{c^2} \frac{1}{\exp\left(\frac{hv}{k_B T}\right) - 1}
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="inline"><mrow><mi>B</mi><mo stretchy="false">(</mo><mi>v</mi><mo>,</mo><mi>T</mi><mo stretchy="false">)</mo><mo>=</mo><mfrac><mrow><mn>2</mn><mi>h</mi><msup><mi>v</mi><mn>3</mn></msup></mrow><mrow><msup><mi>c</mi><mn>2</mn></msup></mrow></mfrac><mfrac><mrow><mn>1</mn></mrow><mrow><mi>exp</mi><mrow><mo stretchy="true" fence="true" form="prefix">(</mo><mfrac><mrow><mi>h</mi><mi>v</mi></mrow><mrow><msub><mi>k</mi><mi>B</mi></msub><mi>T</mi></mrow></mfrac><mo stretchy="true" fence="true" form="postfix">)</mo></mrow><mo>−</mo><mn>1</mn></mrow></mfrac></mrow></math>